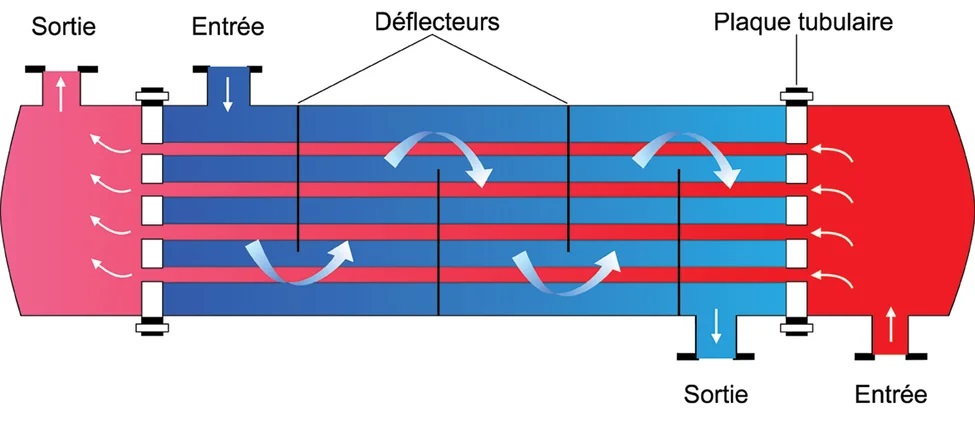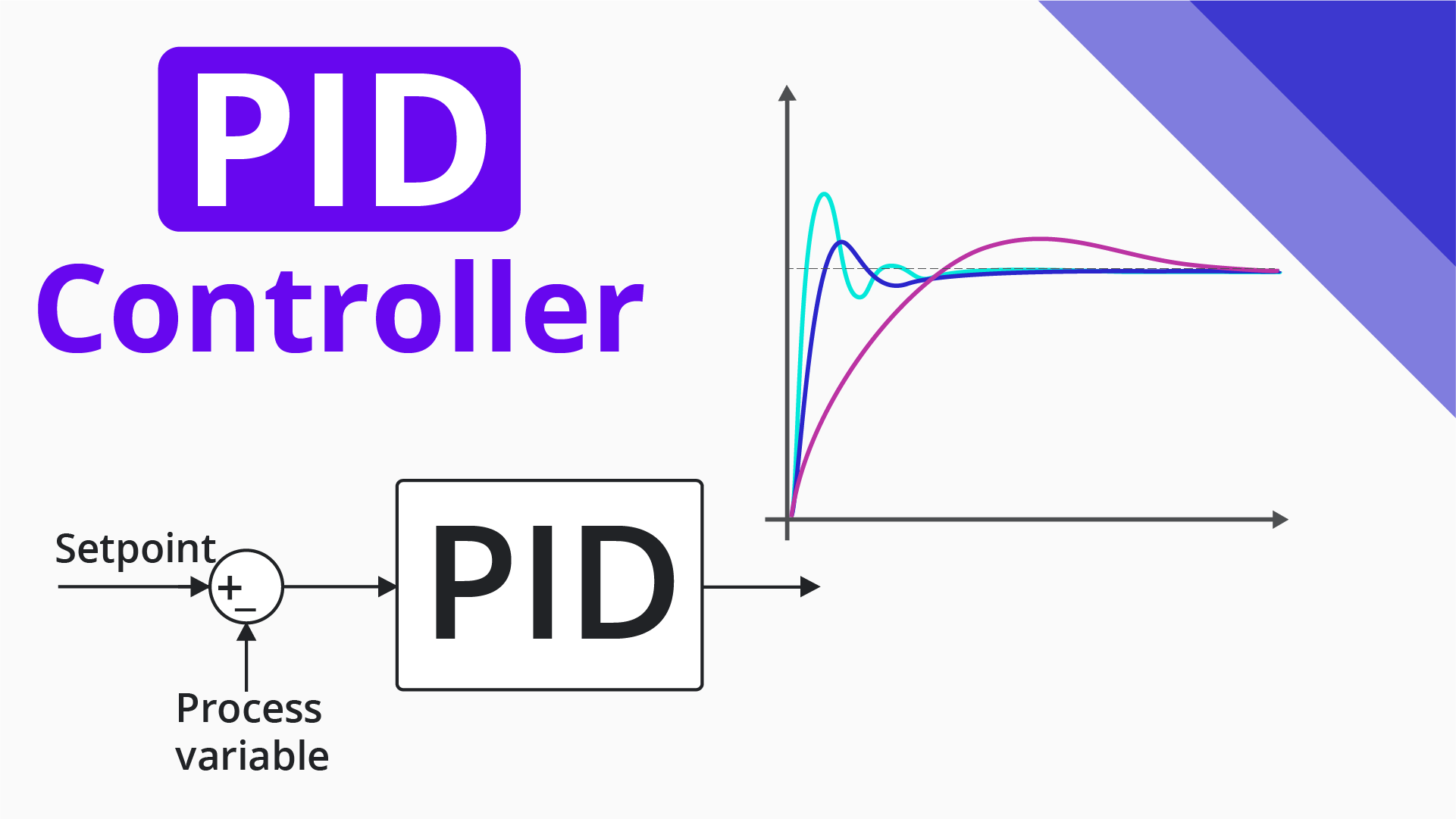
This course offers a comprehensive introduction to the principles and techniques of control systems, with a focus on automatic and linear system regulation. It begins by defining automatic systems and exploring fundamental control structures, namely open-loop and closed-loop systems, highlighting their components—sensors, controllers, and actuators—and their respective advantages and limitations. The course then progresses to the mathematical modeling of linear systems using differential equations and the Laplace transform, providing essential tools for system analysis in the frequency domain. Through the derivation of transfer functions and the study of block diagrams, students learn how to represent and analyze dynamic systems, simplify control structures, and evaluate system performance in terms of stability, accuracy, and responsiveness. Practical examples and schematic representations reinforce understanding of real-world applications such as level control, motor speed regulation, and automation in industrial processes.
- المعلم: Abdelkader Mahmoudi
- المعلم: Abdelkader Mahmoudi

التحضير للاندماج المهني في نهاية الدراسة من خلال عملية نضج فردية وجماعية.
تنفيذ مشروع ما بعد التخرج (متابعة الدراسة أو البحث عن عمل).
إتقان الأدوات المنهجية اللازمة لتحديد مشروع ما بعد التخرج.
التحضير للبحث عن عمل.
التوعية بريادة الأعمال من خلال تقديم لمحة عامة عن المعرفة الإدارية المفيدة لإنشاء الأنشطة.
- المعلم: Abdelkamel MAAMRI

- المعلم: KHALED MANSOURI