
Le module Logiciels de Simulation vise à initier les étudiants aux outils numériques de modélisation et de simulation des systèmes électro-énergétiques.
L’objectif principal est de permettre aux apprenants de maîtriser les logiciels de calcul et de simulation, en particulier MATLAB, SIMULINK et leurs extensions dédiées telles que Power System Blockset (PSB), tout en découvrant la co-simulation avec d’autres plateformes comme PSim, PSpice, Proteus et Scilab.
Le cours est structuré en sept chapitres progressifs, allant de la prise en main de MATLAB (environnement, variables, graphiques, programmation) jusqu’à la modélisation et simulation complète de systèmes électriques sous SIMULINK et PSB.
L’étudiant développera ainsi des compétences pratiques dans la modélisation, la simulation et l’analyse des systèmes énergétiques complexes à travers des exemples concrets et des travaux dirigés.
Prérequis recommandés : notions de programmation et bases de MATLAB.
Évaluation : examen final (100 %).
- Enseignant: kaid imad eddine
- Enseignant: Abdelmalek GACEM
- Enseignant: slimane touil
- Enseignant: Said CHIKHA
- Enseignant: mida dris
Ce cours vise à former l’étudiant à la conception, au calcul et au dimensionnement des machines électriques selon un cahier des charges précis.
Il couvre les principaux types de machines — transformateurs, machines à courant continu, asynchrones et synchrones — en mettant l’accent sur le choix des matériaux, la conception du bobinage et l’analyse des performances.
À l’issue du module, l’étudiant sera capable de concevoir et sélectionner une machine électrique adaptée à une application donnée, en intégrant les contraintes techniques et énergétiques.
- Enseignant: kaid imad eddine
General introduction chapter provides an introduces the key concepts related to history of
automatic control systems, terminology and definition, concept of systems, dynamic behavior,
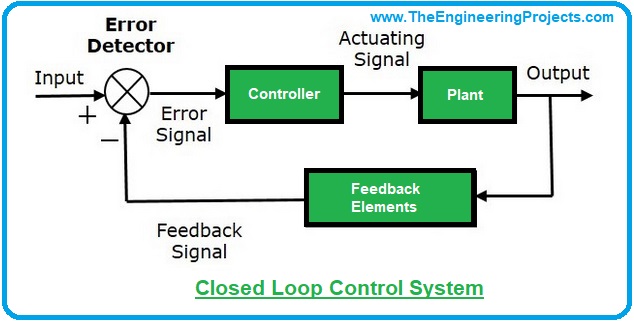
static behavior, static systems, dynamic systems, linear systems, introductory examples, open loop
systems and closed loop systems with performance of servo systems.
Systems modeling chapter focuses on the representation of systems by their differential equations,
Laplace transform, the differential equation to the transfer function, functional blocks and
subsystems, rules of simplification, representation of dynamical systems by fluence graphs,
Mason's rule, calculation of transfer functions of looped systems.
Temporal responses of linear systems chapter: in this chapter, the focus is on the definition of the
response of a system, transient regime, permanent regime, notions of stability, static speed and
accuracy impulse response (1st and 2nd order). temporal characteristics. step response (1st and
2nd order), identification of first and second order systems at from the time response.
Frequency responses of linear systems chapter provides a definition of frequency responses of
linear systems, Bode and Nyquist diagram, Frequency characteristics of systems basic dynamics
(1st and 2nd order), phase and gain margins.
Stability and Accuracy of Servo Systems chapter provides a definition of conditions of stability,
algebraic criterion of Routh-Herwitz, Criteria of the reverse in the Nyquist and Bode plans,
Stability margins, accuracy of servo systems, static accuracy, calculation of the static difference,
dynamic precision.
- Enseignant: lammouchi zakaria

Dans notre vie quotidienne et dans le domaine industriel, nous avons besoin de connaître et de contrôler les grandeurs physiques avec lesquelles nous entrons en contact.
L'utilisation de capteurs reste le moyen optimal pour prélever et mesurer ces grandeurs physiques. Un capteur est un convertisseur qui transforme une information de sa forme physique en un signal (généralement électrique) prêt à être exploité.
Dans ce cours, nous présenterons les capteurs, leurs structures, leurs types et leurs principes de fonctionnement, en abordant également le rôle des capteurs dans les chaînes d'asservissement et de régulation industrielle.
- Enseignant: idriss babaarbi
